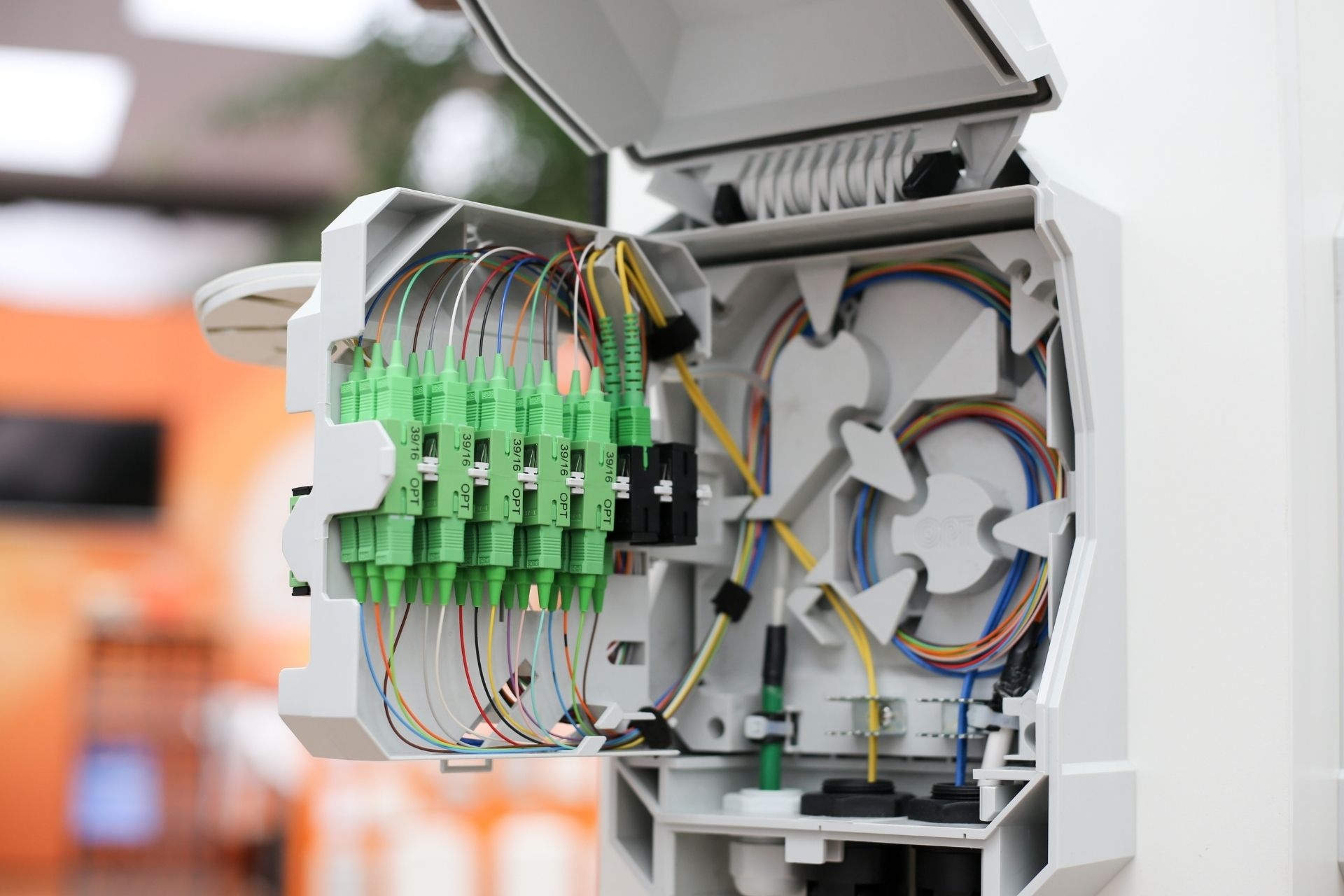
Optical Distribution Frames (ODFs)
What are the different types of connectors used in Optical Distribution Frames (ODFs)?
Optical Distribution Frames (ODFs) typically use various types of connectors such as LC, SC, ST, and MTP/MPO connectors. These connectors play a crucial role in facilitating the connection and transmission of optical fibers within the ODF system. Each type of connector has its own unique design and functionality, allowing for flexibility and compatibility with different types of fiber optic cables.