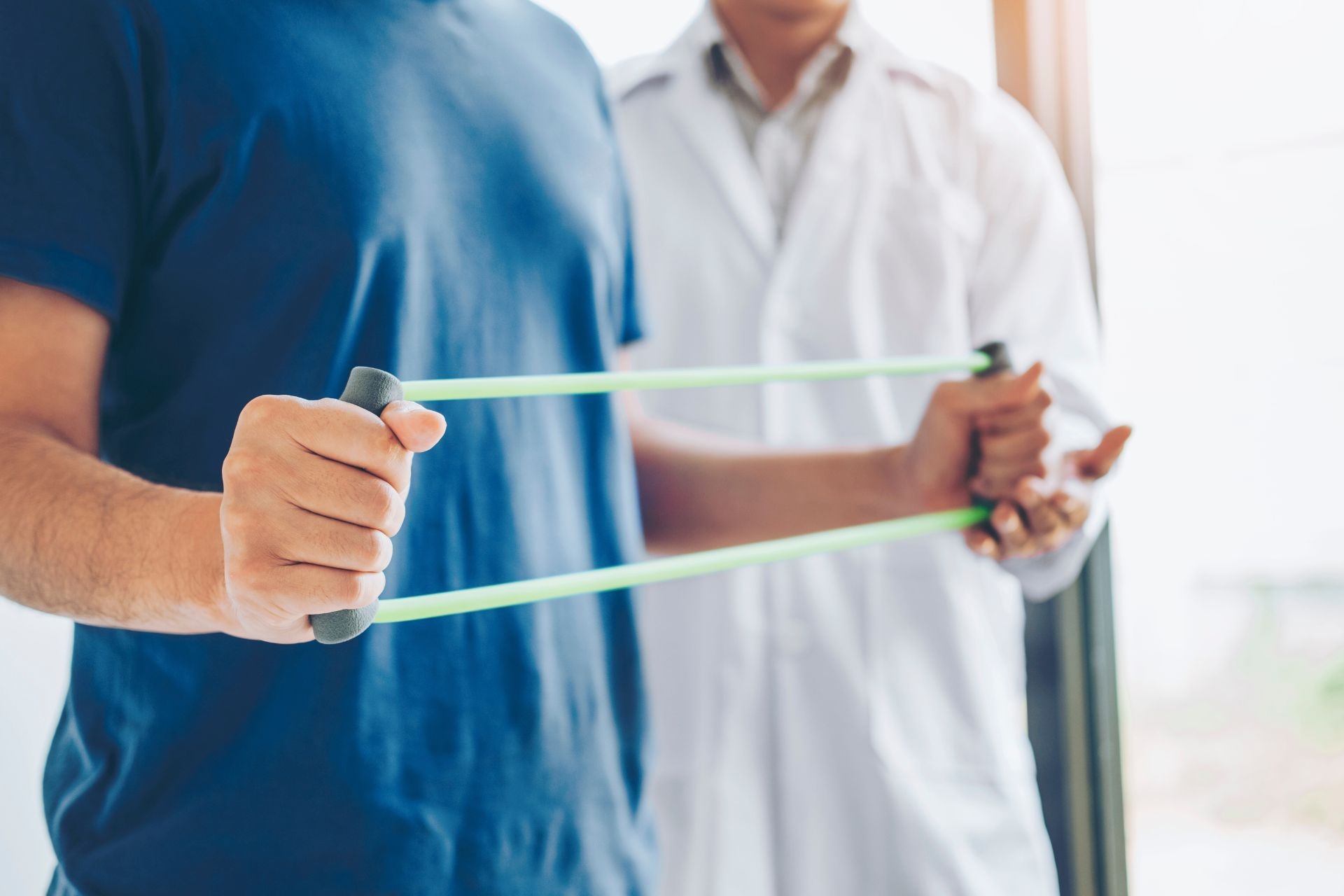


Active myofascial therapy differs from passive myofascial therapy in that it involves active participation from the individual receiving treatment. Active myofascial therapy typically includes movements and exercises performed by the patient under the guidance of a therapist, whereas passive myofascial therapy involves the therapist applying pressure or stretching techniques to the patient's muscles and fascia without their active involvement. Active myofascial therapy aims to improve muscle function, flexibility, and overall movement patterns through active engagement.
Active myofascial therapy can indeed help with specific conditions such as plantar fasciitis or IT band syndrome. By targeting the affected muscles and fascia through active movements and exercises, active myofascial therapy can help release tension, improve flexibility, and reduce pain associated with these conditions. The targeted approach of active myofascial therapy can address the root causes of these issues and promote healing and recovery.
By Professional Physical Therapy Professional Physical Therapy, a leading provider of outpatient physical therapy and rehabilitation services throughout New York, New Jersey, Connecticut, Massachusetts, and New Hampshire, announces the opening of a new state-of-the-art clinic in Livingston, NJ on January 2, 2024. Even more patients in New Jersey will have greater access to the clinical … Continued The post Professional Physical Therapy Opens New Clinic in Livingston, NJ appeared first on Professional Physical Therapy.
Posted by on 2024-01-15
By Professional Physical Therapy As Professional Physical Therapy proudly marks a remarkable milestone of 25 years in the realm of healthcare and wellness, we find ourselves reflecting on the journey that brought us here. To encapsulate the essence of this celebration, we wanted to connect with our co-founder and many of our team members who … Continued The post Celebrating 25 Years at Professional Physical Therapy appeared first on Professional Physical Therapy.
Posted by on 2023-12-27
Common self-care techniques that can complement active myofascial therapy include foam rolling, stretching, and strengthening exercises. These techniques can help maintain the benefits of the therapy between sessions and enhance the overall effectiveness of the treatment. By incorporating self-care practices into their routine, individuals can support the progress made during active myofascial therapy and prevent the reoccurrence of muscle imbalances or restrictions.
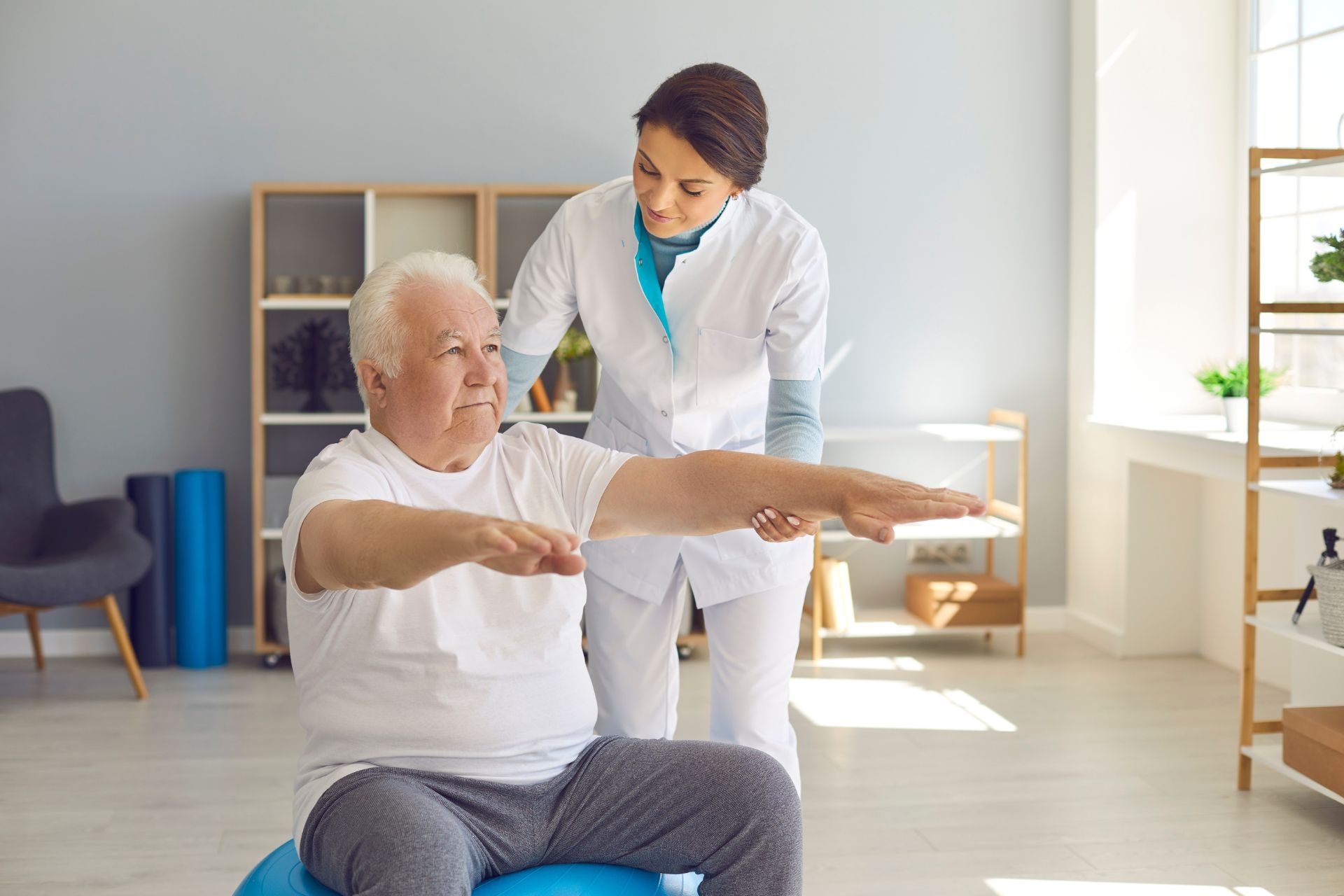

Active myofascial therapy is highly suitable for athletes looking to improve their performance and prevent injuries. By addressing muscle imbalances, restrictions, and areas of tension, active myofascial therapy can enhance muscle function, range of motion, and overall athletic performance. Athletes can benefit from the targeted approach of this therapy to optimize their movement patterns and reduce the risk of injuries during training and competition.
The frequency of active myofascial therapy sessions for optimal results can vary depending on the individual's specific needs and goals. In general, a consistent schedule of sessions, typically ranging from once a week to once a month, may be recommended to maintain progress and address any ongoing issues. The therapist can provide guidance on the ideal frequency of sessions based on the individual's response to treatment and desired outcomes.
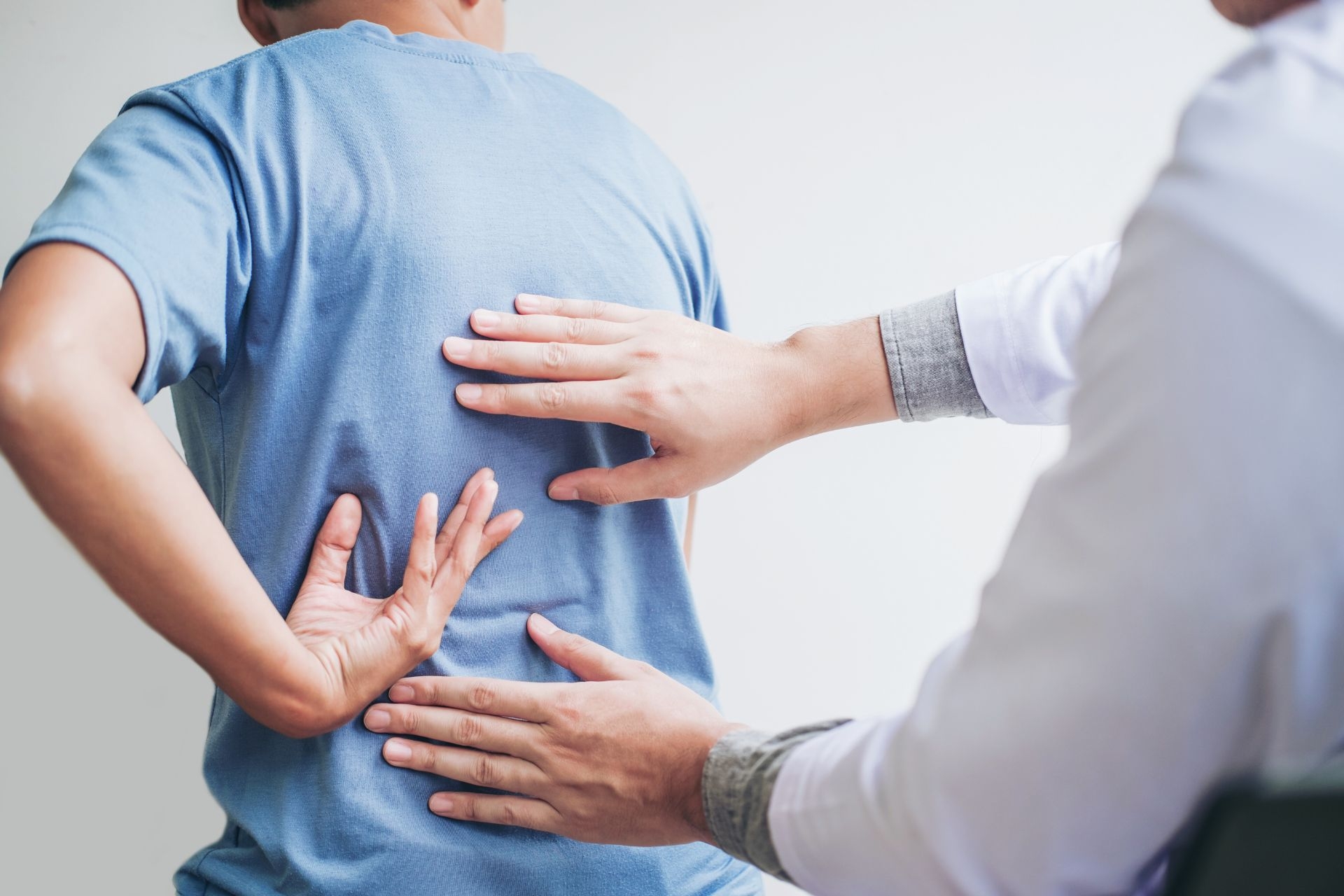
While active myofascial therapy is generally safe and well-tolerated, there are potential risks or side effects to be aware of. These may include temporary soreness, bruising, or increased sensitivity in the treated areas. It is important for individuals undergoing active myofascial therapy to communicate any discomfort or concerns with their therapist to ensure a safe and effective treatment experience. Proper warm-up and cool-down techniques can also help minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Active myofascial therapy can be used as a standalone treatment or combined with other modalities such as massage or stretching for enhanced benefits. Depending on the individual's needs and preferences, a combination of therapies may be recommended to address multiple aspects of muscle and fascial health. Integrating active myofascial therapy with complementary treatments can provide a comprehensive approach to improving movement patterns, reducing pain, and promoting overall well-being.
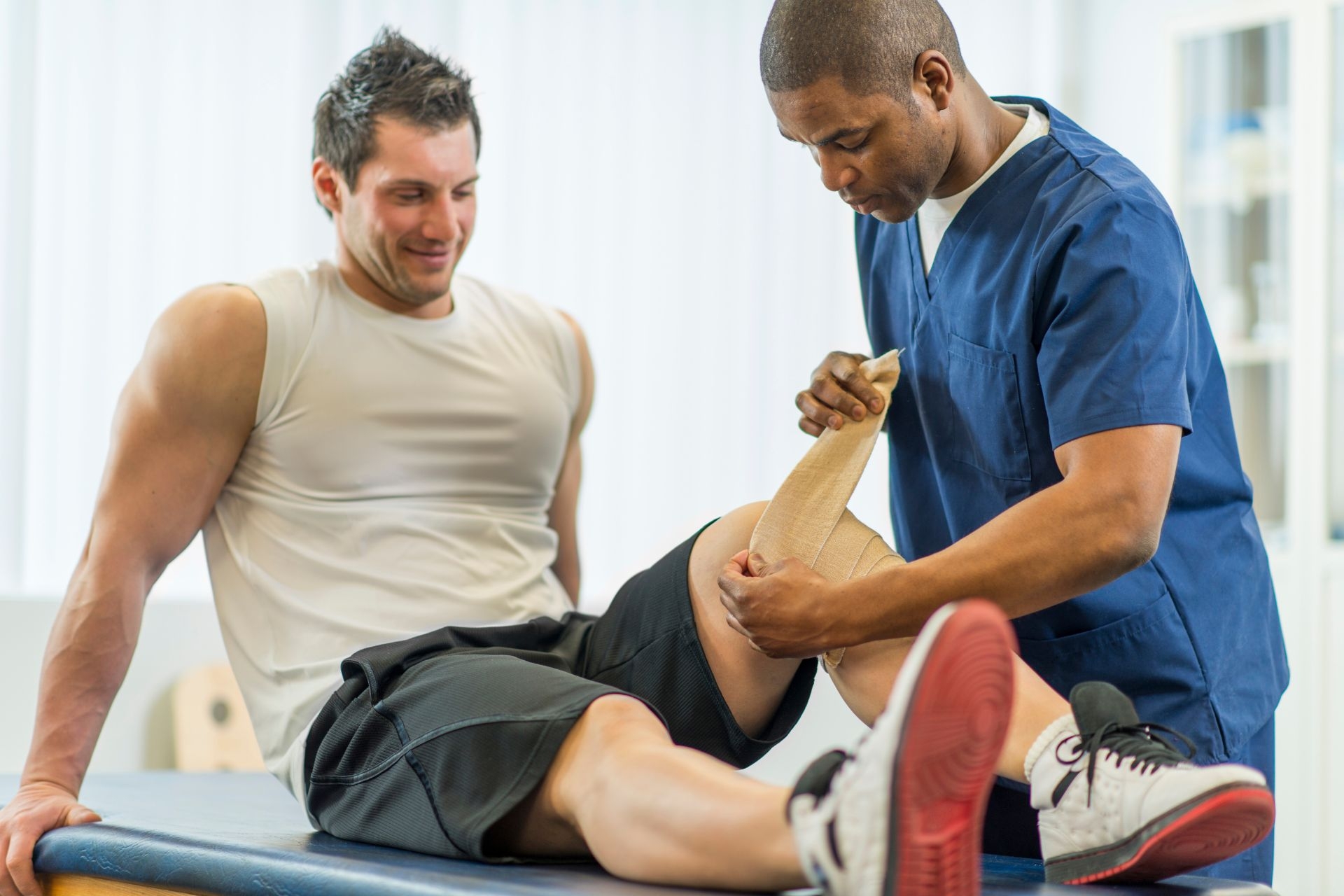
Manual therapy techniques for treating acute lumbar facet joint sprain may include mobilization, manipulation, soft tissue massage, stretching, and therapeutic exercises. These techniques aim to reduce pain, improve range of motion, restore function, and promote healing in the affected facet joint. Mobilization techniques involve gentle, passive movements to help restore normal joint mechanics and reduce inflammation. Manipulation techniques may involve high-velocity, low-amplitude thrusts to realign the facet joint and alleviate pain. Soft tissue massage can help reduce muscle tension and improve circulation to the injured area. Stretching exercises can help improve flexibility and reduce stiffness in the surrounding muscles. Therapeutic exercises may focus on strengthening the core muscles to provide stability and support to the lumbar spine. Overall, a combination of these manual therapy techniques can be effective in treating acute lumbar facet joint sprain.
Ortho-Bionomy differs from traditional manual therapy approaches in several key ways. Unlike conventional methods that focus on applying force or pressure to manipulate tissues, Ortho-Bionomy emphasizes gentle movements and positioning to stimulate the body's self-correcting mechanisms. This approach incorporates principles of osteopathy, chiropractic, and physical therapy to address structural imbalances, pain, and dysfunction. By working with the body's natural alignment and reflexes, Ortho-Bionomy aims to facilitate relaxation, release tension, and promote overall well-being. Additionally, this modality emphasizes the importance of client participation and feedback during sessions, fostering a collaborative and empowering therapeutic relationship. Overall, Ortho-Bionomy offers a unique and holistic approach to manual therapy that prioritizes the body's innate ability to heal and restore balance.
Manual therapy, such as massage, joint mobilization, and stretching, can be beneficial in treating sports-related injuries by improving range of motion, reducing pain, and promoting healing. Techniques like myofascial release, trigger point therapy, and proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation can target specific muscles and tissues affected by the injury. Additionally, manual therapy can help address imbalances, muscle tightness, and scar tissue that may be contributing to the injury. By incorporating manual therapy into a comprehensive treatment plan, athletes can expedite their recovery process and improve their overall performance on the field or court.
Manual therapy techniques can be used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan for sports-related concussions. These techniques may include craniosacral therapy, myofascial release, and cervical spine manipulation. Craniosacral therapy focuses on the gentle manipulation of the skull and sacrum to improve the flow of cerebrospinal fluid and reduce tension in the head and neck. Myofascial release targets the connective tissue surrounding muscles to release tension and improve circulation. Cervical spine manipulation aims to realign the vertebrae in the neck to reduce headaches and improve overall function. These manual therapy techniques can help alleviate symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and neck pain commonly associated with concussions, promoting faster recovery and return to sports activities.