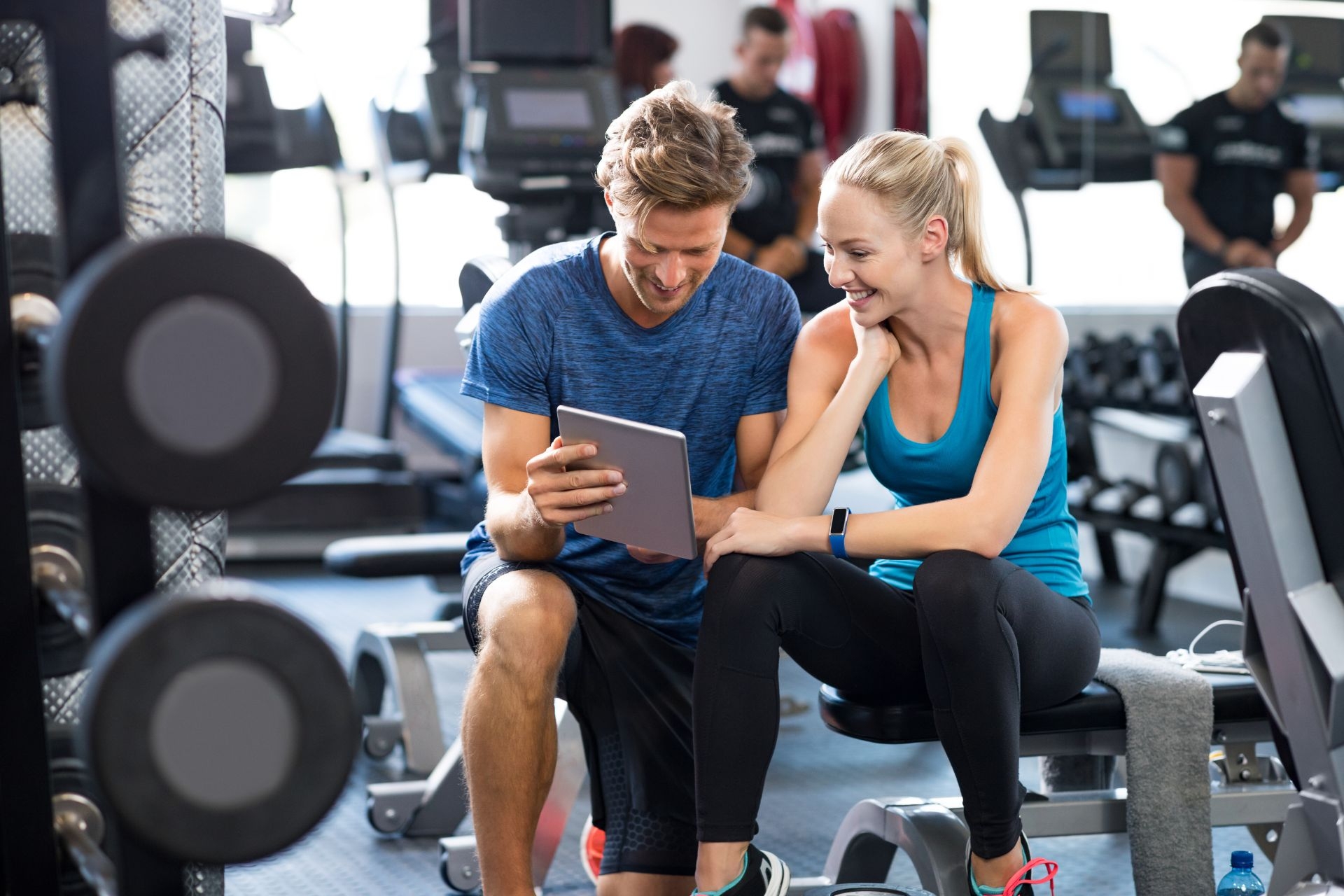


Muscle Energy Technique (MET) helps improve muscle flexibility by utilizing the patient's own muscle contractions to release tightness and increase range of motion. By engaging the muscle in a controlled manner against resistance, MET can help lengthen and relax the muscle fibers, leading to improved flexibility and reduced stiffness. This technique is particularly beneficial for individuals looking to address specific areas of tightness or limited mobility in their muscles.
MET can indeed be used to treat specific muscle imbalances in athletes. By targeting the affected muscles through precise movements and contractions, MET can help restore balance and symmetry to the musculoskeletal system. This can be especially useful for athletes who may have developed imbalances due to repetitive movements or overuse of certain muscle groups. By addressing these imbalances, athletes can improve their overall performance and reduce the risk of injuries.
By Professional Physical Therapy Occupational therapy and physical therapy are essential for recovering from injuries or improving physical conditions, but it’s often associated with repetitive exercises that might be dull or mundane. However, what if we told you that your rehabilitation program could be transformed into a fun experience through gaming? Incorporating games into therapy … Continued The post Game Your Way to Recovery: Fun Games for Physical and Occupational Therapy appeared first on Professional Physical Therapy.
Posted by on 2024-03-19
By Professional Physical Therapy Front shoulder pain is a very common problem. It can come on gradually, over time or suddenly after an injury. Pain in the shoulder may extend down the arm or there may be associated symptoms such as burning pain or numbness. But how do you know what’s wrong? We will look … Continued The post Shoulder Pain in Front: What it Means. appeared first on Professional Physical Therapy.
Posted by on 2024-03-19
By Professional Physical Therapy A pinched nerve in your lower back can be a source of significant discomfort, affecting daily activities and your overall well-being. Common symptoms are the feeling of pins and needles, numbness, burning, and tingling. And sometimes it does not take much to cause it. Poor posture or repetitive activities are enough … Continued The post Understanding and Alleviating the Pain of a Pinched Nerve in Your Back appeared first on Professional Physical Therapy.
Posted by on 2024-02-13
By Professional Physical Therapy Nicolas Fleuriau Chateau is a division 1 soccer player at St. John’s University and one of the top scorers in the country scoring 14 goals (7th in NCAA) in 2023. His story begins in the Spring 2021, when Nick was playing soccer against Syracuse. He was on the field, tried to … Continued The post Nick’s Story: From ACL Rehab at Professional to Major League Soccer Team appeared first on Professional Physical Therapy.
Posted by on 2024-01-24
By Professional Physical Therapy Professional is proud to announce George Papadopoulos, Founding Partner and Chief Development Officer was recognized as one of the top 10 inspiring leaders in 2023 by CLF’s C Level Focus Magazine. C Level Focus magazine is one of the premium business, entrepreneur, technology, leaders’ news publication reaching leaders in the United … Continued The post Professional’s Founding Partner Recognized as Top 10 Inspiring Leader in 2023 appeared first on Professional Physical Therapy.
Posted by on 2024-01-22
The key principles behind MET include active patient participation, precise positioning, and controlled muscle contractions. By actively involving the patient in the treatment process, MET promotes a sense of empowerment and engagement in their own healing. The precise positioning ensures that the targeted muscle is effectively engaged, while the controlled contractions help release tension and improve flexibility. These principles work together to make MET a highly effective technique for improving muscle function.
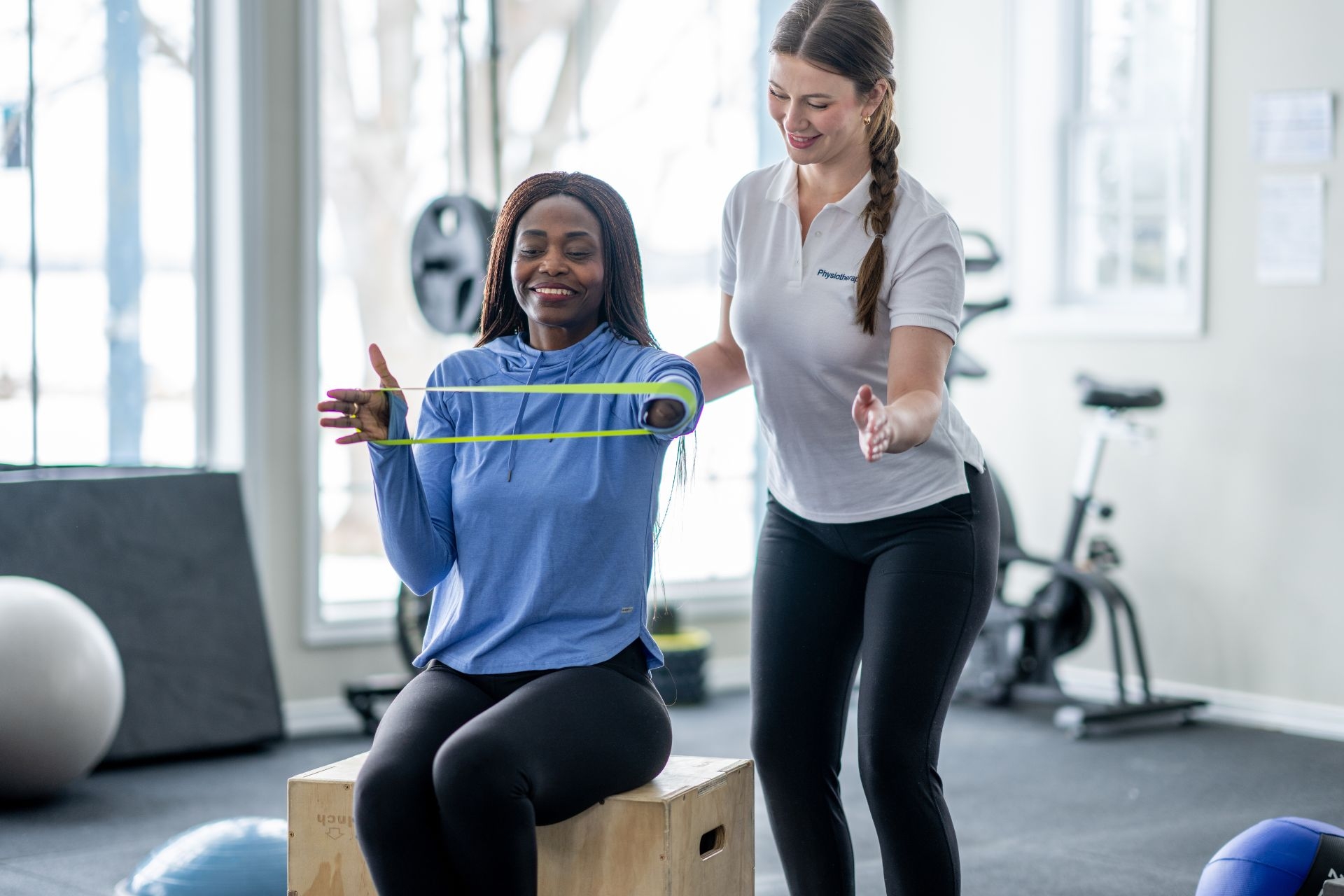

When using MET, it is important to consider any contraindications or precautions for certain muscle groups. For example, individuals with certain medical conditions or injuries may not be suitable candidates for MET, as it involves active muscle contractions that could exacerbate their condition. Additionally, caution should be taken when applying MET to muscles that are already strained or injured, as this could potentially worsen the injury. It is crucial to assess each individual case carefully and adapt the technique accordingly.
MET differs from other manual therapy techniques such as myofascial release or trigger point therapy in its emphasis on active patient participation and muscle contractions. While myofascial release focuses on releasing tension in the fascia surrounding the muscles, and trigger point therapy targets specific points of muscle tightness, MET involves the patient actively engaging their muscles to improve flexibility and function. This active component sets MET apart and makes it a valuable tool for addressing muscle imbalances and restrictions.
MET can be used as a preventative measure to reduce the risk of muscle injuries in physically active individuals. By incorporating MET into a regular maintenance routine, individuals can address any areas of tightness or limited mobility before they develop into more serious issues. This proactive approach can help athletes and active individuals maintain optimal muscle function and prevent injuries that may result from imbalances or restrictions in the muscles.
Research studies have been conducted to support the efficacy of MET in improving muscle function and range of motion. These studies have shown that MET can lead to significant improvements in muscle flexibility, strength, and overall function. By incorporating MET into a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals can experience enhanced performance, reduced pain, and improved quality of life. The evidence supporting the effectiveness of MET continues to grow, making it a valuable tool for healthcare professionals and individuals seeking to optimize their muscle health.
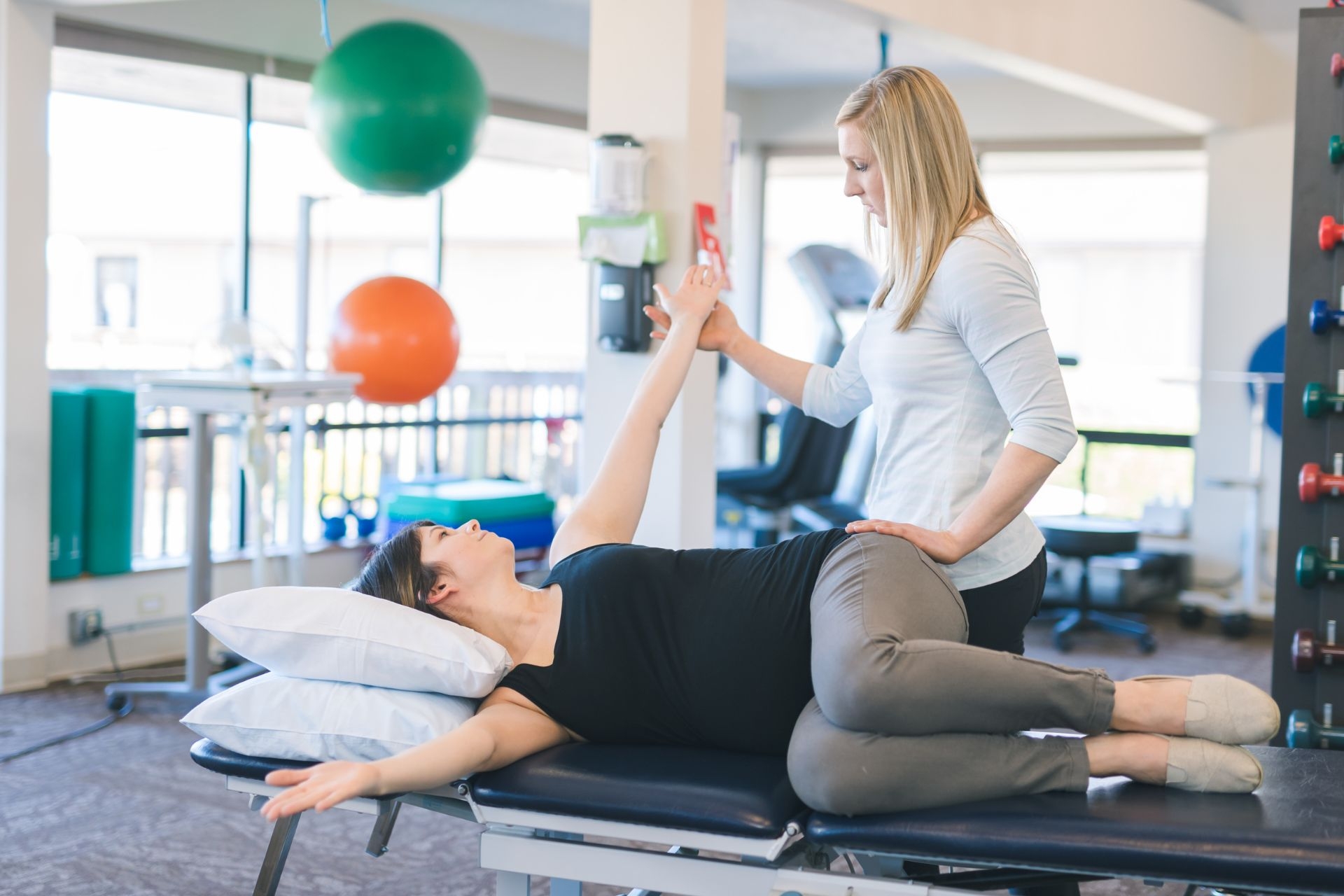

Manual therapy techniques recommended for post-surgical rehabilitation may include soft tissue mobilization, joint mobilization, myofascial release, and scar tissue massage. These techniques can help improve range of motion, reduce pain and inflammation, promote tissue healing, and restore normal movement patterns following surgery. Additionally, manual therapy may involve stretching exercises, proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) techniques, and manual traction to further enhance the rehabilitation process. It is important for a qualified physical therapist or healthcare provider to assess the individual's specific needs and tailor a manual therapy program accordingly to optimize recovery and functional outcomes post-surgery.
Manual therapy techniques such as joint mobilization, soft tissue mobilization, and stretching exercises can be beneficial for improving mobility in elderly patients. These techniques involve hands-on manipulation of the joints and muscles to help increase range of motion, reduce stiffness, and improve overall function. By targeting specific areas of the body that are restricted or tight, manual therapy can help older individuals regain flexibility and movement in their joints. Additionally, techniques like myofascial release and proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation can also be used to address mobility issues in the elderly population. Overall, manual therapy can play a crucial role in enhancing mobility and quality of life for older adults.
The Postural Restoration Institute (PRI) distinguishes itself from other manual therapy approaches through its emphasis on addressing asymmetrical patterns, neuromuscular imbalances, and respiratory influences on posture and movement. PRI utilizes a holistic approach that integrates concepts from biomechanics, neurology, and respiratory science to assess and treat the body as a whole system. By focusing on restoring optimal alignment, breathing patterns, and neuromuscular coordination, PRI aims to address the root causes of dysfunction rather than just treating symptoms. This comprehensive approach sets PRI apart from more traditional manual therapy techniques that may only target specific areas of pain or dysfunction without considering the interconnectedness of the body's systems.
Manual therapy techniques that are suitable for treating whiplash injuries include spinal manipulation, soft tissue mobilization, myofascial release, trigger point therapy, and joint mobilization. These techniques aim to reduce pain, improve range of motion, decrease muscle tension, and promote healing in the affected areas. Additionally, techniques such as active release therapy, proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation, and muscle energy techniques can also be beneficial in addressing the specific needs of individuals with whiplash injuries. It is important for healthcare providers to assess the individual's condition and tailor the manual therapy approach to meet their unique needs and goals for recovery.
Manual therapy, such as massage, stretching, and joint mobilization, can be beneficial in improving athletic performance in runners by addressing musculoskeletal imbalances, reducing muscle tension, increasing flexibility, and promoting better range of motion. By targeting specific areas of the body that may be tight or restricted, manual therapy can help runners optimize their biomechanics, prevent injuries, and enhance overall performance. Additionally, manual therapy techniques can aid in recovery post-run by promoting circulation, reducing inflammation, and alleviating muscle soreness. Incorporating manual therapy into a runner's training regimen can lead to improved running efficiency, speed, endurance, and overall athletic success.