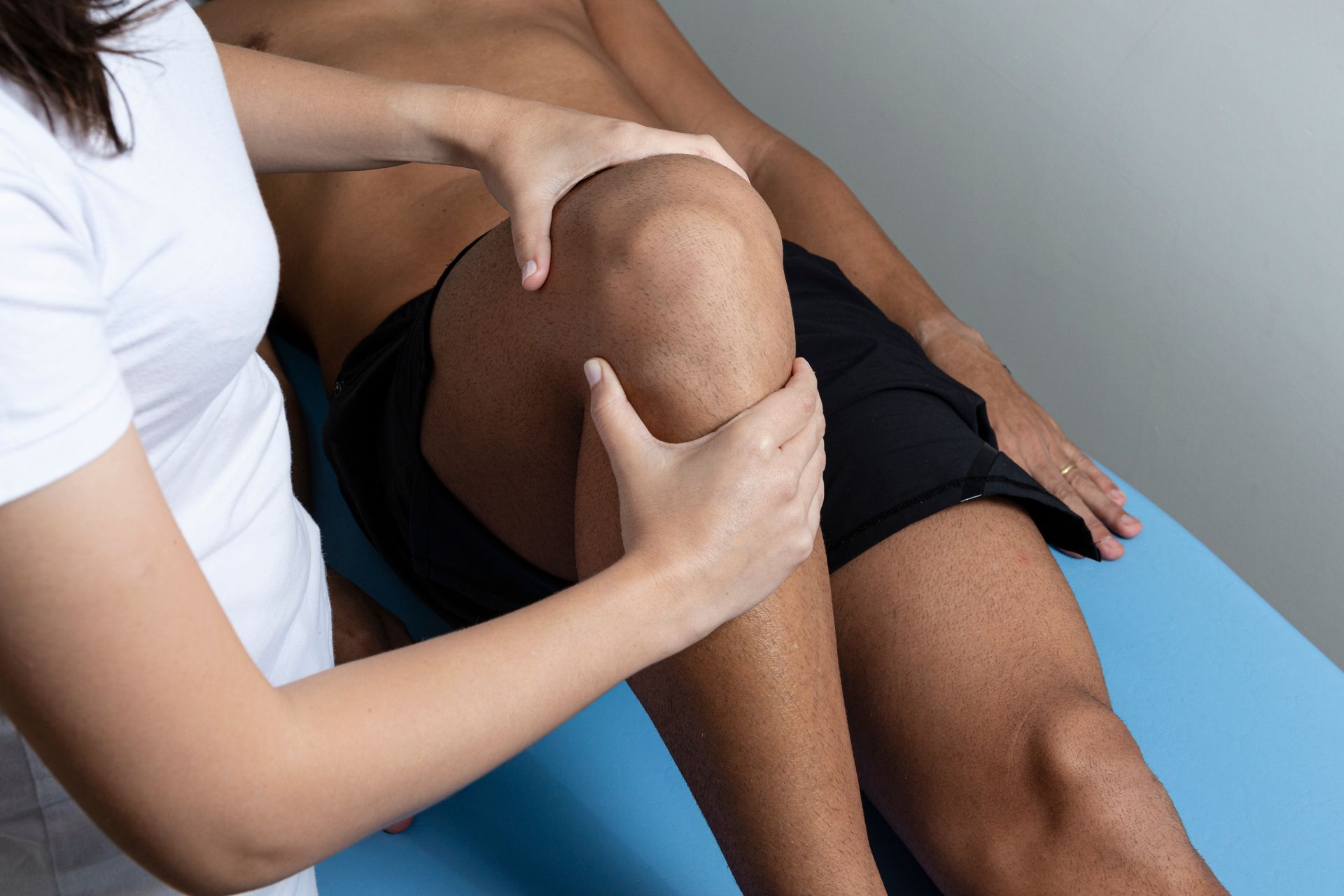

Joint mobilization differs from joint manipulation in terms of the techniques used and the goals of the treatment. Joint mobilization involves passive movement of a joint within its normal range of motion to help improve flexibility, reduce pain, and restore function. On the other hand, joint manipulation involves a high-velocity, low-amplitude thrust to a joint beyond its normal range of motion to correct alignment issues and restore joint function.
There are different grades of joint mobilization techniques that therapists can use depending on the patient's condition and the desired outcome. Grade I mobilization involves small oscillations at the beginning of the range of motion, while Grade II mobilization involves larger oscillations within the mid-range. Grade III mobilization involves large oscillations at the end of the range, and Grade IV mobilization is a sustained stretch at the end of the range.
By Professional Physical Therapy A healthy heart is the cornerstone of overall well-being, and taking proactive steps to maintain cardiovascular health is crucial for a long and vibrant life. This is a particularly important message because heart disease is the leading cause of death in our country. The good news is that many causes of … Continued The post 7 Essential Tips to Keep Your Heart Healthy appeared first on Professional Physical Therapy.
Posted by on 2024-01-15
By Professional Physical Therapy Occupational therapy and physical therapy are essential for recovering from injuries or improving physical conditions, but it’s often associated with repetitive exercises that might be dull or mundane. However, what if we told you that your rehabilitation program could be transformed into a fun experience through gaming? Incorporating games into therapy … Continued The post Game Your Way to Recovery: Fun Games for Physical and Occupational Therapy appeared first on Professional Physical Therapy.
Posted by on 2024-03-19
Joint mobilization can be used to treat conditions like osteoarthritis or frozen shoulder by helping to improve joint mobility, reduce pain, and restore function. By gently mobilizing the affected joint, therapists can help increase synovial fluid production, reduce inflammation, and improve joint lubrication, which can all contribute to relieving symptoms and improving overall joint health.
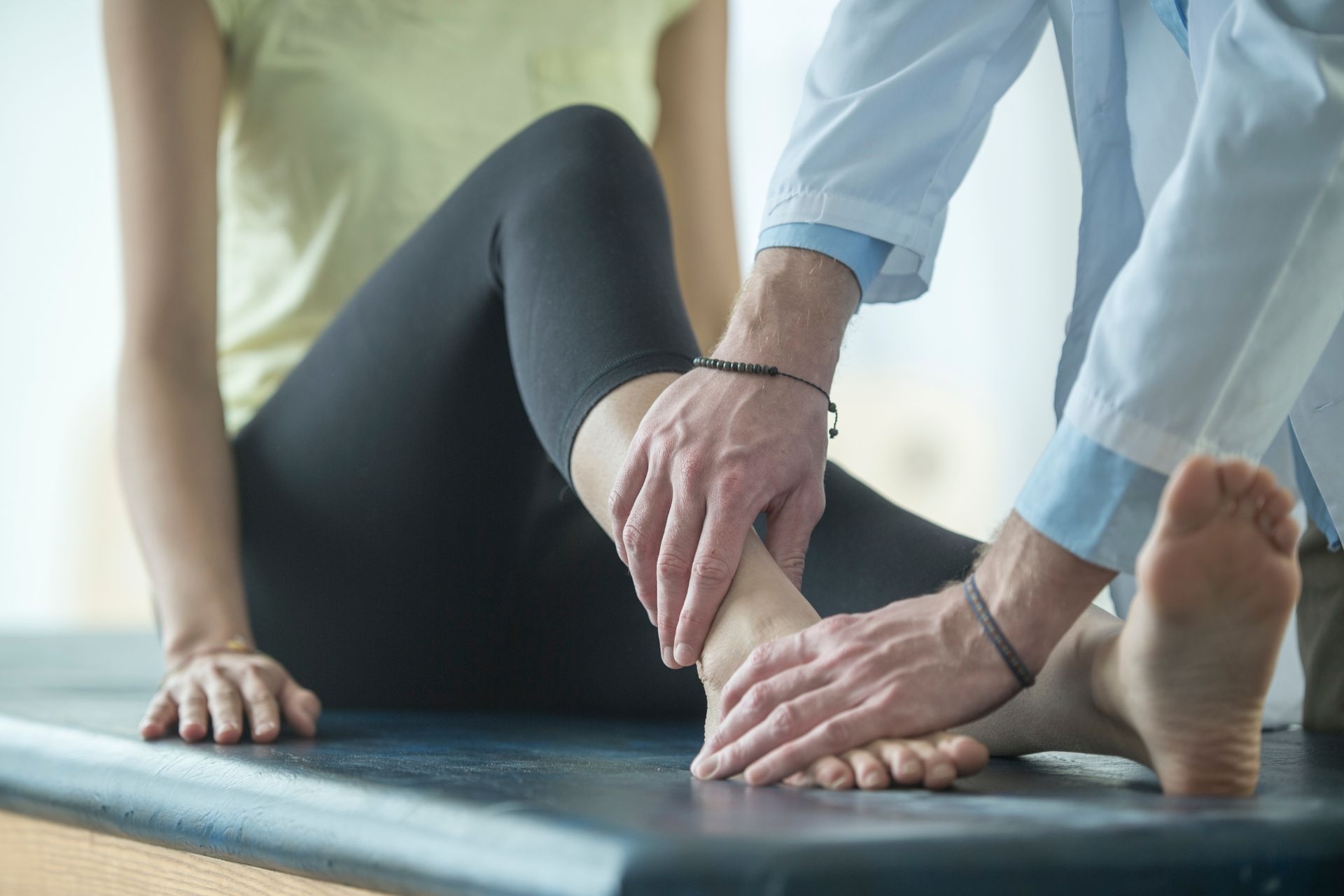

There are certain contraindications for using joint mobilization, such as acute inflammation, fractures, ligamentous instability, and certain medical conditions like osteoporosis. It is important for therapists to carefully assess each patient's condition and medical history before performing joint mobilization to ensure that it is safe and appropriate for the individual.
Joint mobilization helps improve joint range of motion by stretching the surrounding soft tissues, breaking up adhesions, and promoting synovial fluid production. By gently mobilizing the joint through its full range of motion, therapists can help restore normal joint mechanics, reduce stiffness, and improve flexibility, which can ultimately lead to improved function and reduced pain.
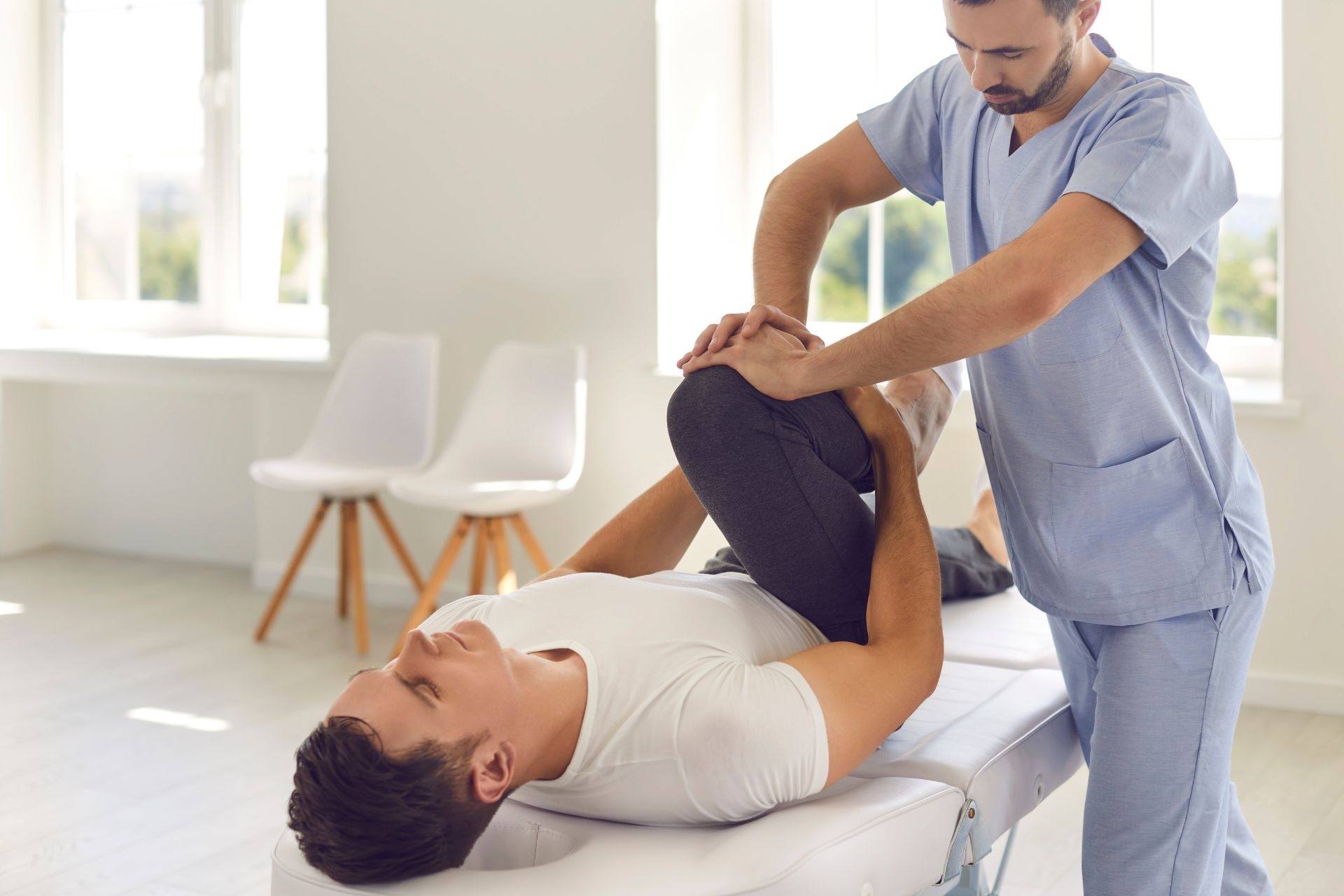
There are specific joint mobilization techniques for different joints in the body, such as the shoulder, knee, hip, spine, and ankle. Each joint has its own unique anatomy and range of motion, so therapists must use specific techniques and approaches to effectively mobilize each joint and address any restrictions or limitations that may be present.
The therapist's assessment plays a crucial role in determining the appropriate joint mobilization technique to use. By conducting a thorough evaluation of the patient's condition, including range of motion, strength, pain levels, and functional limitations, therapists can tailor their treatment approach to address the specific needs of the individual. This personalized approach helps ensure that the joint mobilization techniques used are safe, effective, and targeted towards achieving the best possible outcomes for the patient.
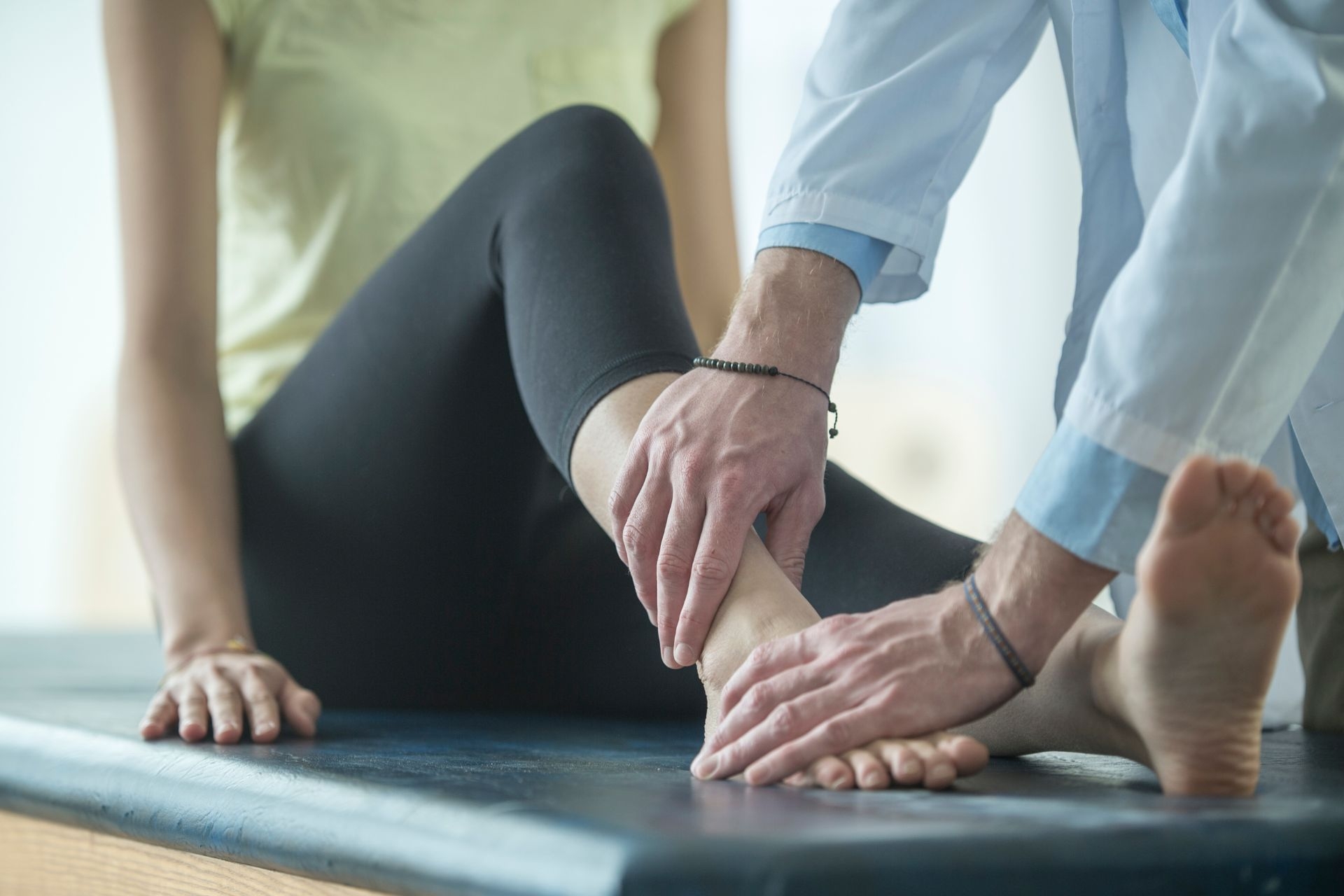

Neurokinetic Therapy (NKT) aids in pinpointing muscular imbalances by utilizing manual muscle testing to assess the function of individual muscles and their corresponding relationships within the kinetic chain. By identifying dysfunctional movement patterns and compensations, NKT practitioners can determine which muscles are overactive (facilitated) and which are underactive (inhibited). This process allows for the root cause of the imbalance to be addressed, rather than just treating the symptoms. Through the use of precise muscle testing and corrective exercises, NKT helps to reprogram the neuromuscular system and restore proper movement patterns, ultimately leading to improved function and reduced risk of injury.
Manual therapy techniques that are suitable for addressing lumbar facet joint syndrome include spinal manipulation, mobilization, soft tissue massage, stretching exercises, and joint mobilization. These techniques can help improve joint mobility, reduce pain, and restore function in individuals with facet joint syndrome. Additionally, techniques such as myofascial release, trigger point therapy, and proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation can also be beneficial in addressing the underlying issues associated with lumbar facet joint syndrome. It is important for a qualified healthcare provider to assess the individual's condition and tailor a treatment plan that includes a combination of these manual therapy techniques to effectively manage facet joint syndrome.
Manual therapy techniques such as deep tissue massage, myofascial release, joint mobilizations, and stretching exercises are considered effective in addressing plantar fasciitis. These techniques help to reduce muscle tension, improve flexibility, and increase blood flow to the affected area, promoting healing and reducing pain. Additionally, manual therapy can help correct any biomechanical imbalances that may be contributing to the condition. By targeting the plantar fascia, calf muscles, and surrounding tissues, manual therapy can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall function in individuals suffering from plantar fasciitis. It is important for a trained therapist to assess the individual's specific needs and tailor the treatment plan accordingly to achieve optimal results.
Fascial Manipulation stands out from other manual therapy modalities due to its focus on the manipulation of the fascia, a connective tissue that surrounds muscles, bones, and organs. Unlike traditional massage therapy or chiropractic adjustments, Fascial Manipulation targets specific points within the fascia to release tension, improve mobility, and restore proper function. This technique involves a deep understanding of the anatomy and biomechanics of the body, allowing practitioners to address underlying issues that may be causing pain or dysfunction. By addressing the fascia directly, Fascial Manipulation can provide long-lasting relief and improve overall movement patterns. Additionally, this modality emphasizes the importance of individualized treatment plans tailored to each patient's unique needs, ensuring a comprehensive and effective approach to manual therapy.