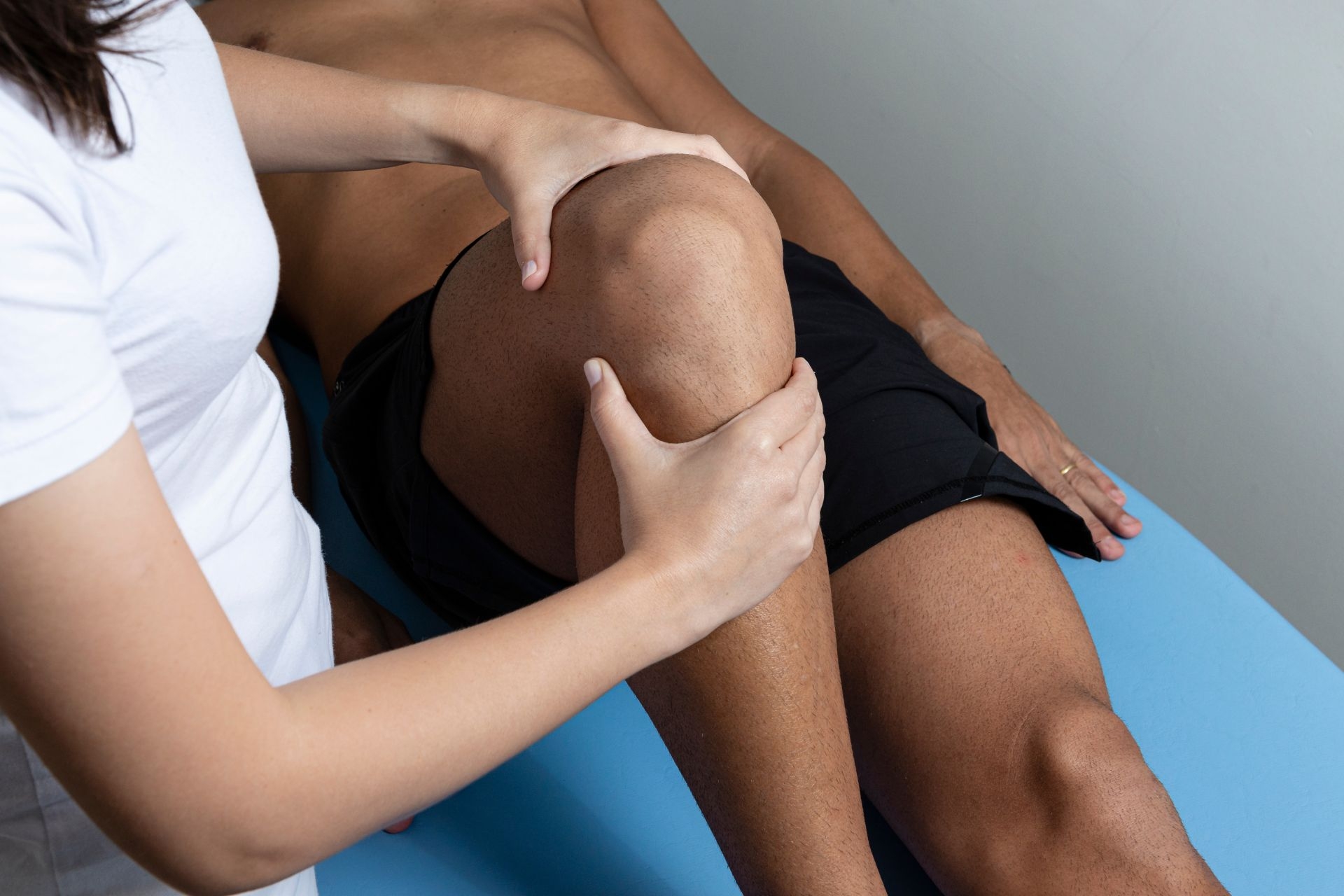

Facilitated Stretch Therapy (FST) differs from traditional stretching techniques in that it involves a therapist actively assisting the client in moving through a series of stretches, rather than the individual performing the stretches on their own. This hands-on approach allows for a deeper stretch and targets specific muscle groups more effectively, leading to increased flexibility and range of motion.
FST can indeed help improve flexibility in specific muscle groups by targeting those areas with precise stretches and movements. The therapist can tailor the session to focus on particular muscles that may be tight or restricted, helping to release tension and improve overall flexibility. This targeted approach can be especially beneficial for athletes or individuals looking to enhance their performance in specific activities.
By Professional Physical Therapy As Professional Physical Therapy proudly marks a remarkable milestone of 25 years in the realm of healthcare and wellness, we find ourselves reflecting on the journey that brought us here. To encapsulate the essence of this celebration, we wanted to connect with our co-founder and many of our team members who … Continued The post Celebrating 25 Years at Professional Physical Therapy appeared first on Professional Physical Therapy.
Posted by on 2023-12-27
Incorporating FST into a regular fitness routine can offer a range of benefits, including improved flexibility, reduced risk of injury, enhanced athletic performance, and increased relaxation. By regularly participating in FST sessions, individuals can work towards achieving their flexibility goals while also promoting overall well-being and physical health.
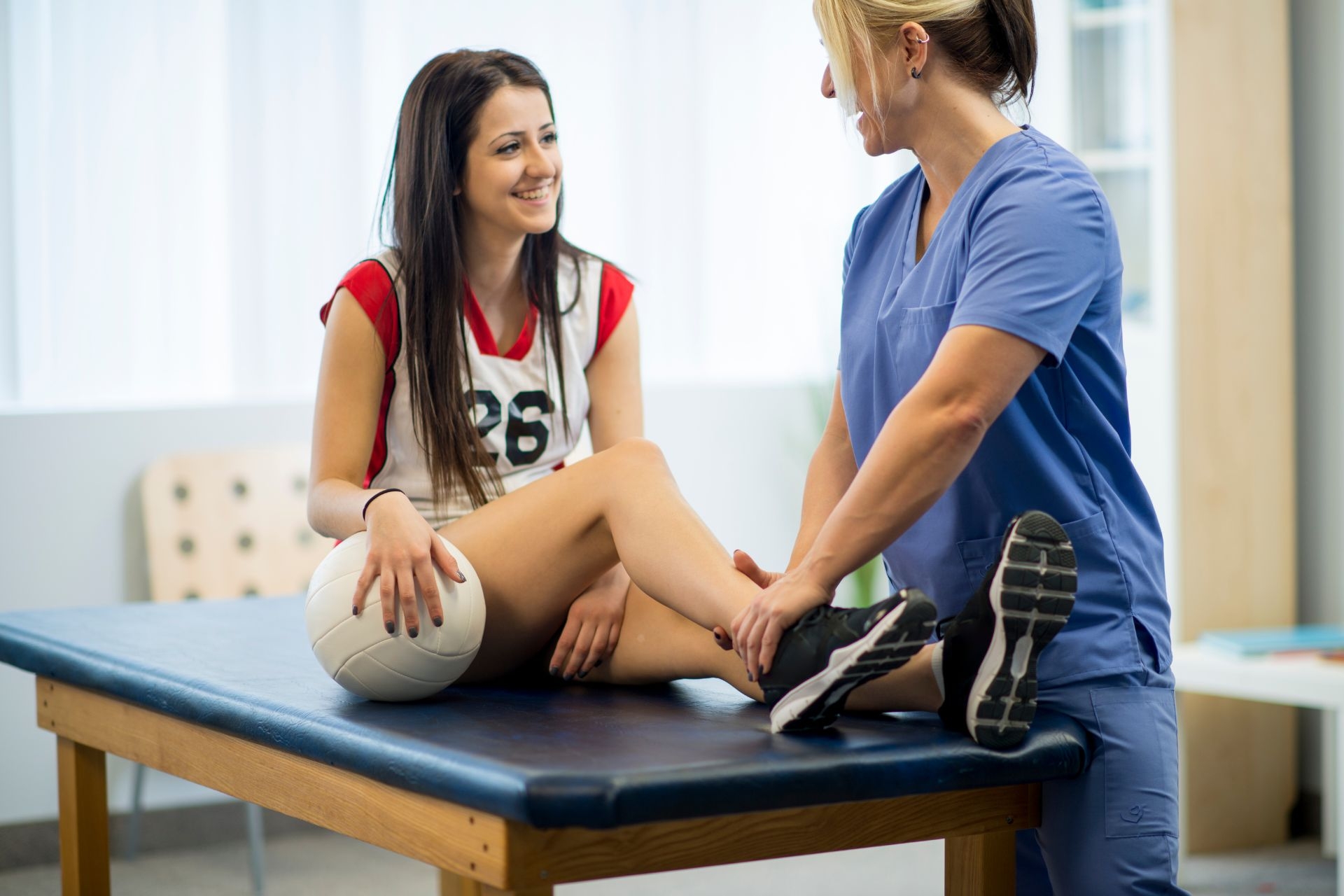

FST can be suitable for individuals recovering from injuries or with limited mobility, as the therapist can adapt the stretches to accommodate the individual's needs and limitations. By gently guiding the client through the stretches, FST can help improve mobility, reduce stiffness, and aid in the rehabilitation process.
FST targets fascia and connective tissue in the body by using specific stretching techniques that focus on elongating and releasing tension in these areas. By addressing the fascia and connective tissue, FST can help improve overall flexibility, reduce muscle tightness, and enhance movement patterns.
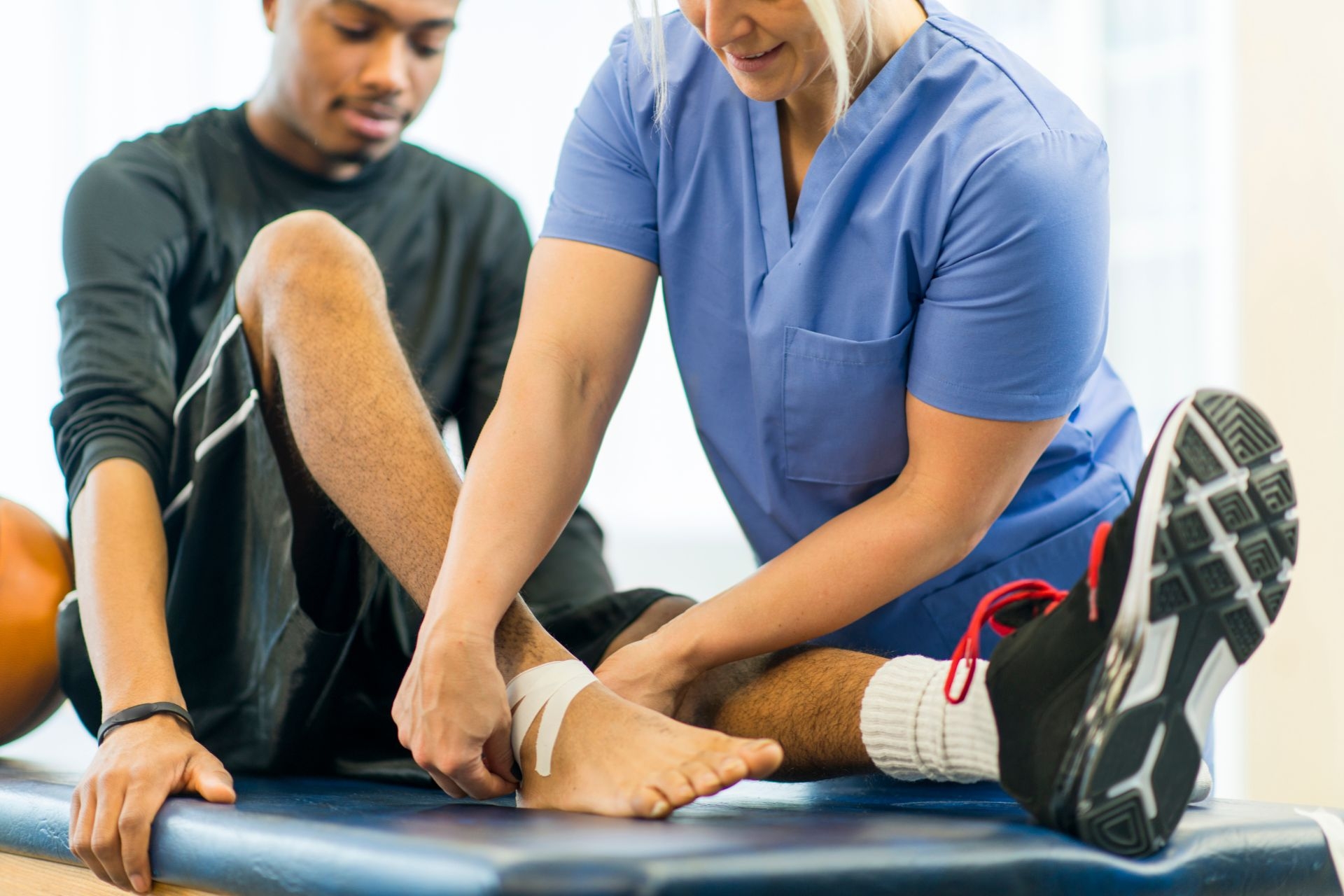
Before trying FST, it is important to consider any contraindications or precautions that may apply. Individuals with certain medical conditions, injuries, or limitations may need to consult with a healthcare provider before participating in FST to ensure that it is safe and appropriate for their specific situation.
To see noticeable results from FST, individuals may benefit from participating in sessions on a regular basis. The frequency of sessions can vary depending on individual goals and needs, but consistent participation in FST can help maintain and improve flexibility over time. It is recommended to work with a qualified therapist to develop a personalized plan that aligns with individual goals and preferences.

The contraindications for Graston Technique include acute fractures, open wounds, active infections, deep vein thrombosis, cancer, and compromised skin integrity. Individuals with a history of blood clotting disorders, peripheral neuropathy, or severe osteoporosis should also avoid this treatment. Additionally, patients with a pacemaker or other electronic implant should not undergo Graston Technique due to the risk of interference. It is important for healthcare providers to thoroughly assess each patient's medical history and current health status before recommending or performing this manual therapy technique.
Manual therapy techniques for treating shoulder impingement may include soft tissue mobilization, joint mobilization, myofascial release, and stretching exercises. These techniques aim to improve range of motion, reduce pain, and restore proper alignment of the shoulder joint. Manual therapy can also help address muscle imbalances, improve posture, and enhance overall shoulder function. Additionally, specific techniques such as cross-friction massage, passive range of motion exercises, and proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) stretching may be utilized to target the affected muscles and structures involved in shoulder impingement. By incorporating a combination of these manual therapy techniques, healthcare providers can effectively address the underlying issues contributing to shoulder impingement and promote optimal recovery and rehabilitation.
Manual therapy techniques such as manual lymphatic drainage (MLD), compression therapy, and exercise have been shown to be effective in improving lymphatic circulation in lymphedema patients. MLD involves gentle, rhythmic massage movements that help stimulate the lymphatic system and promote the flow of lymph fluid. Compression therapy, which includes the use of compression garments or bandages, helps to reduce swelling and improve lymphatic drainage. Additionally, exercise can help improve muscle pump function, which aids in lymphatic circulation. Other manual therapy techniques, such as skin care and breathing exercises, can also play a role in managing lymphedema and improving lymphatic circulation in affected individuals.
Structural Integration, also known as Rolfing, can benefit chronic tension headaches by addressing the underlying structural imbalances in the body that may be contributing to the pain. By focusing on realigning the fascia, muscles, and joints, Structural Integration can help improve posture, reduce muscle tension, and increase overall body awareness. This can lead to decreased stress on the neck and shoulders, which are common areas of tension for those suffering from chronic headaches. Additionally, by improving overall body alignment and movement patterns, Structural Integration can help prevent future headaches from occurring. By addressing the root cause of the tension headaches, rather than just treating the symptoms, Structural Integration offers a holistic approach to managing chronic pain.
When using Unwinding in manual therapy, practitioners must take several precautions to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the technique. It is important to assess the patient's range of motion, flexibility, and any underlying conditions before performing Unwinding. Practitioners should also communicate clearly with the patient throughout the process to ensure their comfort and understanding of the technique. Proper body mechanics and positioning are crucial to prevent injury to both the practitioner and the patient. Additionally, it is essential to start with gentle movements and gradually increase intensity to avoid causing any discomfort or pain. Monitoring the patient's response and adjusting the technique as needed is also important to achieve optimal results. Overall, following these precautions can help maximize the benefits of Unwinding in manual therapy while minimizing the risk of adverse effects.
Rolfing Structural Integration can benefit posture alignment by addressing imbalances in the body's myofascial system, promoting proper alignment of the skeletal structure, and improving overall body awareness. Through targeted manual manipulation of the fascia, Rolfers can release tension and restrictions that may be pulling the body out of alignment. By realigning the body's structure, Rolfing can help improve posture, reduce pain, and enhance movement efficiency. Additionally, Rolfing sessions often include movement education and postural re-education to help clients maintain the benefits of the structural work long-term. Overall, Rolfing Structural Integration can play a significant role in improving posture alignment and overall body function.